
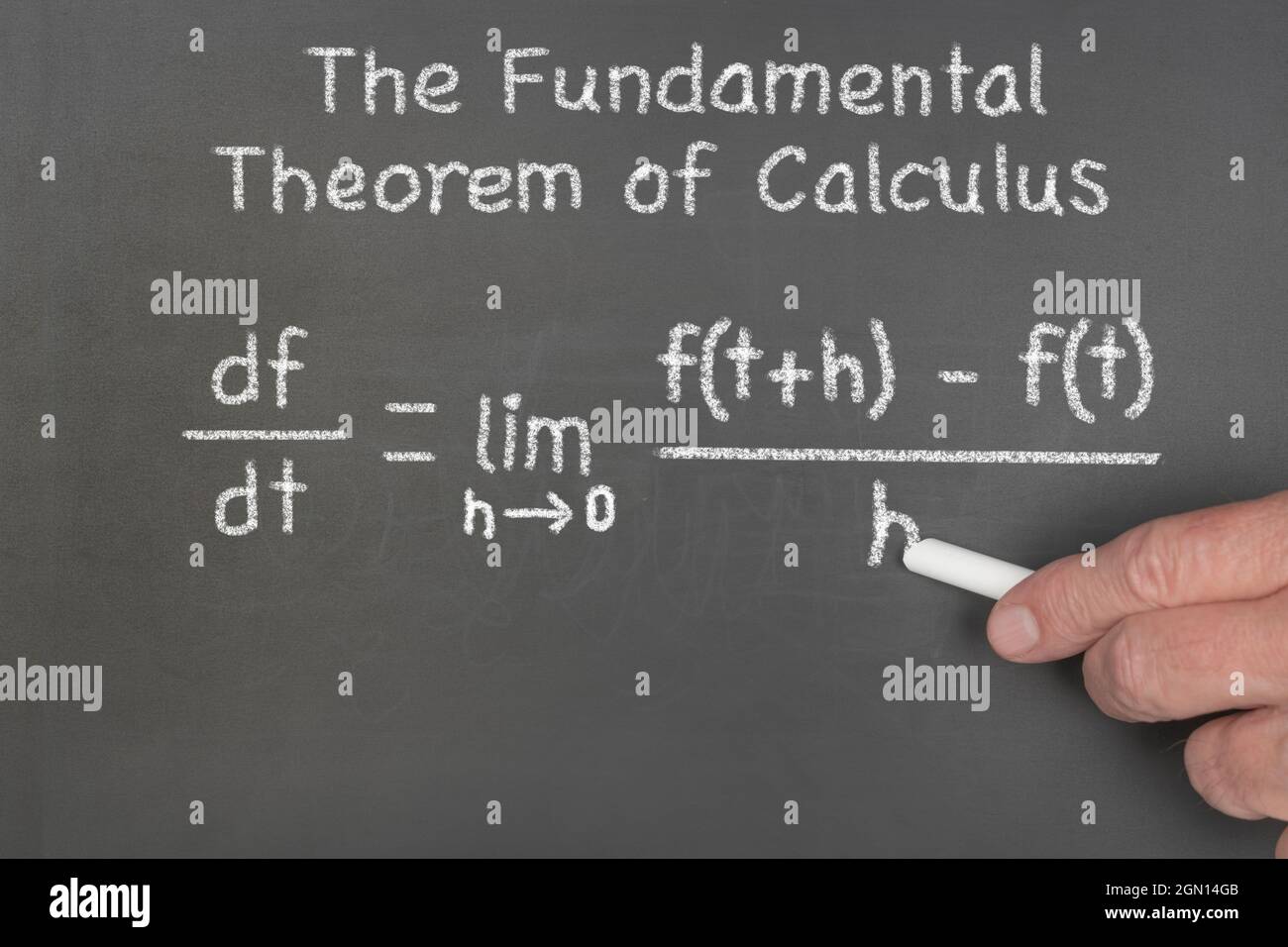
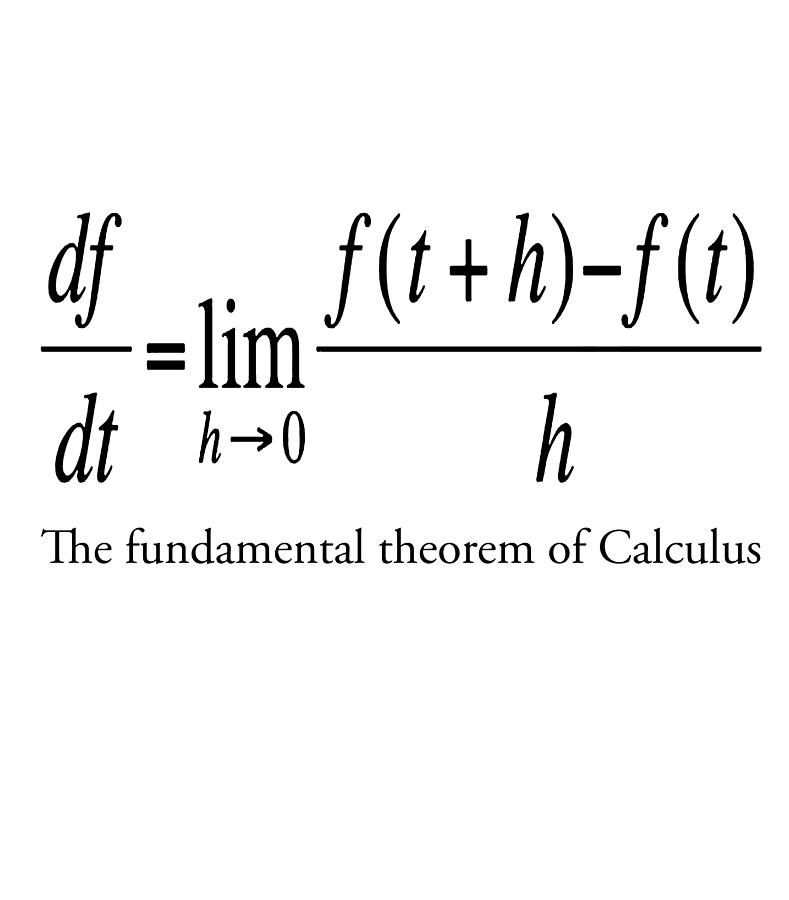
MathType on Twitter: "A classic we never covered and the bane of many high school students: The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. The culmination of work by Gregory, Barow, Newton, Leibniz and more

integration - Second fundamental theorem of calculus for function of two variables - Mathematics Stack Exchange

Applied calculus; principles and applications . mum according to the fundamental test. Again,there are exceptional non-algebraic functions for which/ (x),as X increases through some finite value a, changes sign GRAPHICAL ILLUSTRATION

PDF) The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus: The Chain Rule and Integration by substitution A brief Compendium by Newton The Principia Mathematica














![1.3.2 The fundamental theorem of differentials [FTD] - ppt download 1.3.2 The fundamental theorem of differentials [FTD] - ppt download](https://slideplayer.com/slide/15434094/93/images/7/Poincar%C3%A9+lemma+and+converse.jpg)